ERP systems serve as a central hub for all business data, providing real-time information and analytics to support decision-making. They eliminate data silos and reduce the need for manual data entry, minimizing errors and improving overall data accuracy. By providing a holistic view of business operations, ERP systems enable organizations to optimize their processes, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a comprehensive software system that integrates and manages core business processes across an organization. ERP software combines various functions such as finance, human resources, supply chain management, and customer relations into a single, unified platform. This integration allows for seamless data flow and improved efficiency in business operations.
Key Differences between ERP and CRM
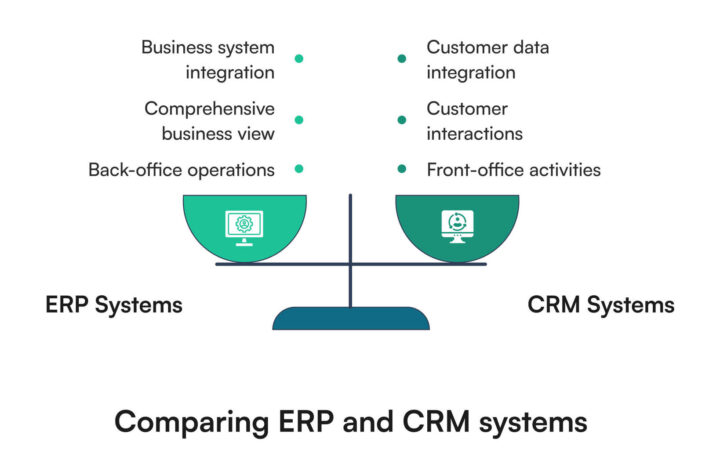
While Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) focuses on managing overall business processes, Customer Resource Management (CRM) software specifically targets customer interactions and relationships. ERP systems often include CRM functionality, but dedicated CRM solutions offer more specialized features for customer management.
ERP systems primarily deal with back-office operations such as finance, HR, and supply chain management. They provide a comprehensive view of the entire business operation. CRM systems, on the other hand, focus on front-office activities like sales, marketing, and customer service. They help organizations manage customer interactions, track sales pipelines, and improve customer satisfaction.
Integration capabilities. ERPs can integrate with other business systems and external data sources, enabling a more comprehensive view of operations and enhancing functionality.
Sure, CRM is great for managing customer relationships, but ERP? ERP is not just about software; it’s about creating a single source of truth for your entire organisation.

Types of Enterprise Resource Planning Systems
ERP systems are not one-size-fits-all solutions. They come in various types, each designed to meet specific business needs, technological preferences, and industry requirements. This section explores the main categories of ERP systems, helping you understand which type might be the best fit for your organization.
| Type | Description | Best Suited For | Key Advantages | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| On-premise ERP | Installed and run on company's own servers. | Large enterprises with specific customization needs. | Full control over data and system. | High upfront costs, maintenance responsibility |
| Cloud-based ERP | Hosted on remote servers, accessed via internet. | Small to medium businesses, companies valuing flexibility. | Lower upfront costs, automatic updates. | Potential data security concerns, less customization. |
| Hybrid ERP | Combines on-premise and cloud elements | Organizations requiring both control and flexibility. | Balances control and accessibility. | Complexity in managing dual systems. |
| Generic ERP | Broad functionality applicable to various industries. | Businesses with standard operational needs. | Wide range of features, often more affordable. | May lack industry-specific features. |
| Industry-specific ERP | Tailored for particular sectors. | Businesses in specialized industries (e.g., healthcare, manufacturing). | Aligned with industry-specific needs and regulations. | Can be more expensive, potentially over-specialized. |
Many organizations use both ERP and CRM systems, often integrating them to provide a complete view of business operations and customer relationships.
How Does ERPs Work?
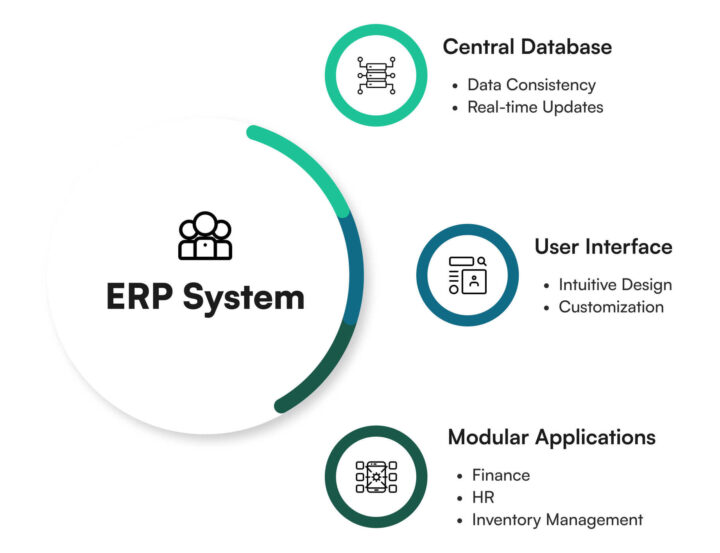
ERP systems operate by centralizing data and processes across different departments. They typically include modules for various business functions, each sharing information through a common database. This structure enables real-time data access and analysis, facilitating informed decision-making and streamlined operations.
Main steps of ERP:
- Central database. This is the core of the ERP system, storing all data from various modules in a single location. It ensures data consistency and enables real-time updates across all departments.
- User interface. The interface allows users to interact with the system, input data, and access information. Modern ERP systems often feature intuitive, customizable interfaces to enhance user experience and productivity.
- Modular applications. These are specialized components designed for specific business functions such as finance, HR, or inventory management. Modules can be added or removed based on the organization’s needs.
Reporting tools. ERP systems include robust reporting capabilities, allowing users to generate custom reports, dashboards, and analytics to gain insights into business performance.
The variety of ERP types available ensures that businesses can find a solution that aligns with their specific needs, technological infrastructure, and growth plans. Whether you opt for an on-premise system for maximum control, a cloud-based solution for flexibility, or an industry-specific ERP for tailored functionality, understanding these different types is crucial in making an informed decision. As we proceed to discuss the benefits of ERP systems, consider which type might offer the most advantages for your organization’s unique requirements.
Contact us and we will find the best solution for you
The Key Advantages of ERP Systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems offer a wide array of advantages that can significantly transform business operations. Understanding these benefits is crucial for organizations considering ERP implementation or looking to maximize their existing systems. The following points highlight the key advantages that well-implemented ERP systems can bring to a business.
- Improved efficiency. Streamlines business processes and reduces manual tasks. ERP systems automate many routine operations, freeing up staff time for more strategic activities.
- Enhanced data accuracy. Eliminates data duplication and inconsistencies. With a single source of truth, organizations can trust their data for critical decision-making.
- Better decision-making. Provides real-time insights and analytics. ERP systems offer comprehensive reporting and analysis tools, enabling managers to make informed decisions quickly.
- Increased collaboration. Facilitates information sharing across departments. By breaking down data silos, ERPs promote better communication and teamwork throughout the organization.
- Cost reduction. Optimizes resource allocation and reduces operational expenses. ERPs help identify inefficiencies and streamline processes, leading to significant cost savings over time.
- Scalability. Supports business growth and adaptation to changing needs. ERP systems can be expanded or modified to accommodate new business units, processes, or market conditions.
The benefits of ERP systems extend far beyond simple process automation. By providing a unified platform for data management, decision-making, and operational efficiency, ERPs can drive substantial improvements across all areas of a business. While the initial investment may be significant, the long-term benefits in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and strategic capability often far outweigh the costs.
But let’s be real – implementing an ERP isn’t a walk in the park. It’s a significant investment that comes with its fair share of challenges.

Common ERP Implementation Challenges
While ERP systems offer numerous advantages, it’s essential to also consider the potential challenges and drawbacks associated with their implementation and use. Being aware of these weaknesses allows organizations to better prepare for ERP adoption and develop strategies to mitigate potential issues. The following points outline some of the key challenges businesses may face with ERP systems.
- High implementation costs: Initial investment can be substantial. ERP implementation often requires significant financial resources for software licenses, hardware, and consulting services.
- Complexity: May require extensive training and adaptation. ERP systems can be complex, and users may need time to become proficient with the new system.
- Customization challenges: Modifications can be time-consuming and expensive. Tailoring an ERP system to specific business needs may require significant development work and ongoing maintenance.
- Potential disruption: Implementation may temporarily affect business operations. The transition to a new ERP system can cause short-term productivity losses as employees adapt to new processes.
- Vendor lock-in: Switching to a different system can be difficult and costly. Once an organization has invested in an ERP system, changing to a new vendor can be a complex and expensive process.
While the challenges associated with ERP implementation and use are significant, they are not insurmountable. Many of these weaknesses can be mitigated through careful planning, thorough vendor evaluation, and a well-executed implementation strategy. Organizations should weigh these potential drawbacks against the benefits when deciding on ERP adoption and be prepared to address these challenges proactively throughout the implementation process and beyond.
Strategic Considerations for ERP Selection
Choosing the right ERP system is a critical decision that can significantly impact your business. This section provides key tips to guide your selection process.
Assess your business needs
Identify specific requirements and pain points. Conduct a thorough analysis of your current processes and determine which areas need improvement.
Consider scalability
Ensure the system can grow with your business. Choose an ERP that can accommodate increased data volume and additional users as your organization expands.
Choose a system that will grow with you and work well with your existing technology. And remember, the cheapest option isn’t always the best – consider the long game when crunching the numbers.

Evaluate integration capabilities
Check compatibility with existing systems. Ensure the ERP can integrate seamlessly with your current software applications and databases.
Compare costs
Consider both initial and long-term expenses. Factor in software licenses, implementation costs, training, and ongoing maintenance when evaluating different ERP options.
Review user-friendliness
Ensure the system is intuitive for your team. Choose an ERP with a user-friendly interface to minimize training time and maximize user adoption.
Check customization options
Determine if the ERP can be tailored to your processes. Look for systems that offer flexibility in customizing workflows and reports to match your specific business needs.
Investigate vendor support
Evaluate the quality and availability of technical assistance. Choose a vendor that offers comprehensive support services, including implementation assistance and ongoing technical support.
Assess security features
Ensure data protection and compliance with regulations. Verify that the ERP system has robust security measures in place and complies with relevant industry standards and data protection laws.
Consider mobile accessibility
Look for systems with robust mobile capabilities. In today’s mobile-first world, having access to ERP functions on smartphones and tablets can significantly improve productivity.
Read user reviews
Gather insights from other businesses in your industry. Research customer testimonials and case studies to understand how the ERP system performs in real-world scenarios similar to your own.
Selecting an ERP system is a complex process that requires careful consideration of multiple factors. By following these tips, you can increase your chances of choosing a system that will meet your organization’s needs both now and in the future.
Conclusion
Enterprise Resource Planning systems are powerful tools for businesses seeking to optimize their operations and drive growth. While implementing an ERP system can be a significant undertaking, the potential benefits in terms of efficiency, data management, and decision-making capabilities make it a worthwhile investment for many organizations.
The future of ERP systems is likely to involve increased use of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and predictive analytics to provide even more powerful insights and automation capabilities. As technology continues to evolve, ERP systems will play an increasingly crucial role in helping businesses navigate complex market conditions and stay ahead of the competition.




